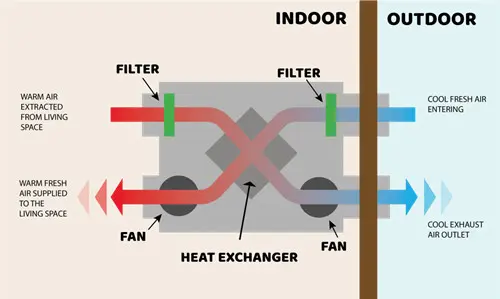
Heat recovery ventilation (HRV), also known as mechanical ventilation heat recovery (MVHR), is an advanced ventilation method designed to improve indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption. In simple terms, a heat recovery ventilation system allows fresh air to enter a building while capturing heat from the outgoing stale air. Instead of losing energy through traditional ventilation methods, HRV units recycle it, resulting in lower heating and cooling demands.
A heat recovery ventilator works by transferring heat from the exhaust air to the incoming fresh air, ensuring that energy is not wasted. This process makes HRV one of the most effective and eco-friendly technologies in modern building design.
The basic principle of a heat recovery ventilation unit is straightforward but highly efficient. The system typically consists of:
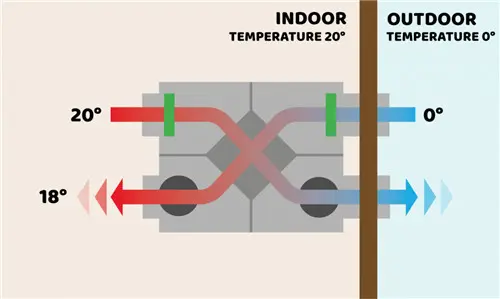
When warm air is expelled from the building, it passes through the heat exchanger. At the same time, cold fresh air is drawn in. Without the two air streams ever mixing directly, the heat exchanger ventilation process allows heat energy to transfer from the warm exhaust air to the cool incoming air. In summer, the process can work in reverse, helping to pre-cool the incoming air.
This technology allows a heat recovery system to recover between 60% and 95% of the heat from the exhaust air, drastically reducing the energy required to maintain indoor comfort.
A typical mechanical ventilation with heat recovery system includes:
These components work together to provide clean, fresh, and temperature-controlled indoor air with minimal energy loss.

Installing a heat recovery ventilation system provides several important benefits:
By recycling heat that would otherwise be wasted, HRV systems cut down on energy bills and reduce the load on HVAC systems.
A heat recovery ventilator constantly supplies filtered fresh air while removing stale air, improving oxygen levels and reducing pollutants, allergens, and excess humidity.
In winter, incoming air is preheated, reducing drafts and cold spots. In summer, some systems offer partial cooling effects, keeping interiors more comfortable.
With reduced energy consumption, heat recovery ventilation systems help lower a building's carbon footprint, making them a popular choice for green building certifications.
Traditional ventilation methods, such as opening windows or using basic exhaust fans, allow fresh air to enter but lose valuable heat energy in the process. In contrast, a heat recovery ventilation unit not only brings in fresh air but also captures and reuses up to 95% of the heat that would normally be lost.
Compared to a simple ventilation fan or exhaust fan, HRV systems are more sophisticated, energy-saving, and environmentally friendly. This makes them ideal for modern, airtight buildings that require constant airflow without compromising efficiency.
Heat recovery ventilation systems are widely used in both residential and commercial settings:
The flexibility of heat recovery ventilators makes them suitable for almost any building that requires continuous ventilation.
There are different types of heat recovery ventilation units available, depending on the building design and efficiency requirements:
Each system has its own advantages, but all contribute to improved energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
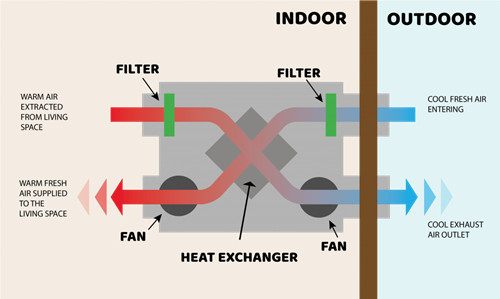
When installing a heat recovery ventilation system, correct sizing and duct design are critical to ensure efficiency. Placement of the heat recovery unit should allow easy access for maintenance.
Key maintenance practices include:
With proper care, an HRV system can last for decades, providing reliable energy savings and improved air quality.
As buildings become more airtight and energy-efficient, indoor air circulation often suffers. Without proper ventilation, humidity, pollutants, and carbon dioxide levels can rise, leading to discomfort and even health risks.
A heat recovery ventilator solves this issue by providing continuous fresh air without wasting valuable energy. Whether for a home, office, or industrial facility, installing a mechanical ventilation with heat recovery system ensures both comfort and sustainability.
At MiWind, we specialize in modern air management solutions, including ventilation fans, air curtains, dehumidifiers, fresh air systems, and advanced heat recovery ventilation units. With over 20 years of experience, we deliver reliable, energy-efficient systems tailored to diverse customer needs.
A heat recovery ventilation system is far more than just a way to move air—it's a smart energy-saving technology that improves comfort, lowers heating and cooling costs, and enhances indoor air quality. By using a heat exchanger ventilation system, buildings can recover up to 95% of wasted energy, making HRV a cornerstone of modern sustainable design.
Whether you call it heat recovery ventilation, mechanical ventilation with heat recovery, or a heat recovery ventilator, this system is one of the most effective investments for creating healthier, greener, and more efficient indoor spaces.