
Heat recovery ventilation systems are engineered to reclaim heat from outgoing stale air and transfer it to incoming fresh air, using a specialized heat exchanger ventilation process that keeps the two air streams separate. This process not only enhances indoor air quality but also significantly reduces the energy needed for heating or cooling spaces. The primary purpose of heat recovery ventilation is to maintain a healthy indoor environment by ensuring a continuous supply of filtered, fresh air while minimizing energy loss associated with traditional ventilation methods.
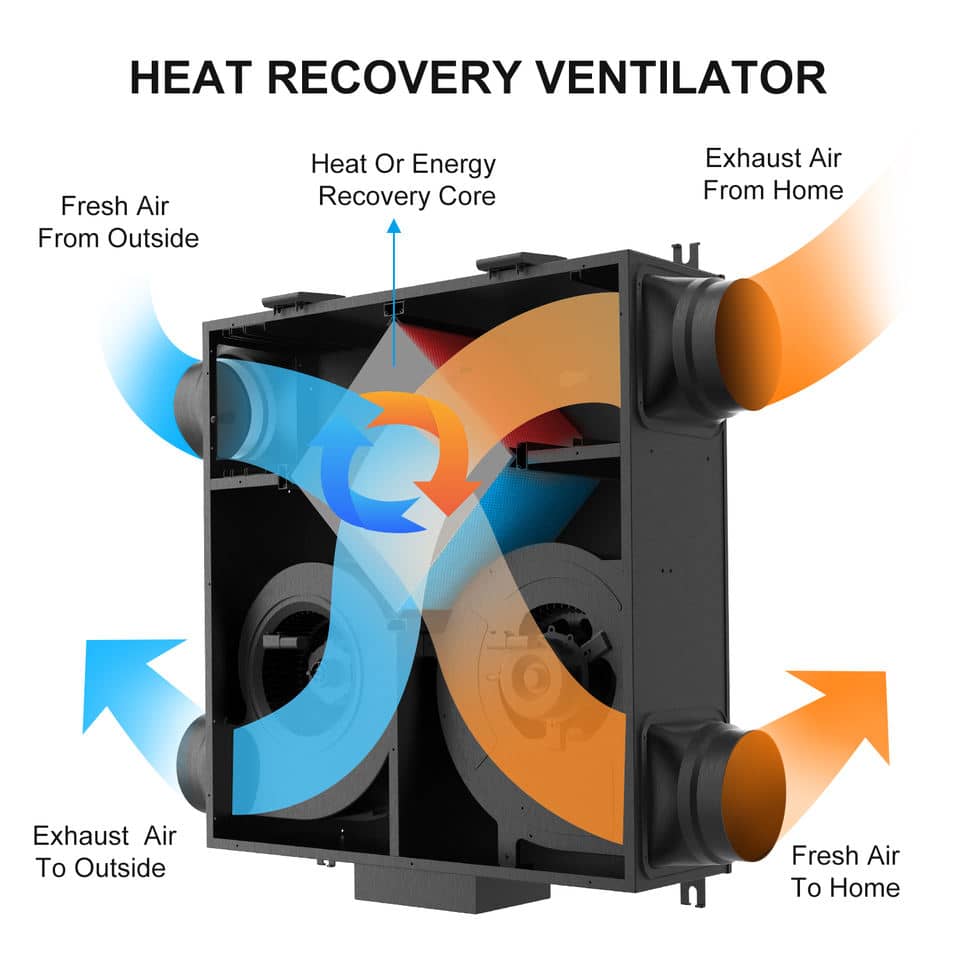
A heat recovery unit operates through a ventilation heat exchanger that transfers thermal energy between the exhaust and supply airstreams.
Exhausting Stale Air: The heat recovery ventilator extracts stale indoor air, which carries away heat.
Heat Exchange: As the warm stale air exits, it passes through a heat exchanger vent, transferring its heat to the incoming cold outdoor air.
Supplying Fresh Air: The now-tempered air is introduced into the living space, minimizing additional heating or cooling.
Modern heat recovery systems can reclaim 60% to 95% of the thermal energy from outgoing air, depending on system design and efficiency.
The following are essential for any heat reclaim ventilation setup:
Heat Exchanger Core: Where thermal exchange between incoming and outgoing air occurs.
Dual Fans: One for expelling stale air, another for drawing in fresh air.
Ductwork Network: Carries the air to and from various rooms.
Air Filters: Clean incoming air of pollutants, allergens, and dust.

A major benefit of heat recovery ventilation systems is their contribution to energy conservation. By recovering heat from exhaust air, heat recovery vents reduce HVAC loads, resulting in lower energy consumption and operating costs.
These systems ensure a steady flow of clean air, reducing harmful contaminants such as VOCs, carbon dioxide, and dust. The result is a fresher, healthier indoor atmosphere.
Balanced ventilation helps regulate humidity levels, preventing mold growth and moisture-related damage.
The heat recovery ventilator system preconditions incoming air, making winter air warmer and summer air cooler, thereby maintaining consistent indoor comfort.
By reducing the need for active heating and cooling, heat exchange ventilation systems lower carbon footprints and contribute to sustainable building practices.

In homes, heat recovery systems are highly valued for their energy-saving benefits and contribution to better air quality—especially in airtight, modern structures.
In offices, schools, and other commercial environments, ventilation heat recovery systems ensure a healthy workspace while managing energy costs efficiently.
In large-scale industrial environments, heat recovery ventilation units handle high volumes of exhaust, reclaiming heat for reuse in other heating or production processes.
Proper installation of a heat recovery ventilation unit involves assessing building size, occupancy, and climate conditions. Strategic ducting and zoning ensure optimal heat recovery.
While generally low-maintenance, systems must be inspected regularly. Replacing clogged filters and checking fan operation will help sustain efficiency and air purity.
Heat Recovery Ventilation systems represent a leap forward in energy-efficient building design. They ensure cleaner air, lower utility costs, and a reduced environmental impact. Whether in homes, offices, or factories, adopting a heat recovery system is a smart investment in comfort, health, and sustainability.
Understanding what a heat recovery ventilator is, how it works, and its numerous benefits can guide homeowners, architects, and builders in choosing the best ventilation solution for modern living.